Ever feel like your phone is hypnotizing you into endless scrolling? Or like that cookie jar whispers your name louder at midnight? Welcome to the world of the Charles Duhigg Habit Loop, where your brain quietly controls your life without asking for permission.
Habits are strong. They shape your everyday existence, often without you noticing. According to study, around 40% of your everyday behaviors aren’t decisions, they’re habits on autopilot. Understanding this cycle is crucial to correcting negative habits or reinforcing positive ones. Whether you’re attempting to quit smoking, start exercising, or just stop procrastinating, learning the Charles Duhigg Habit Loop can give you the upper hand. Ready to discover how your brain works? Let’s dig in.
Psychology of Habits: What is the Charles Duhigg Habit Loop?
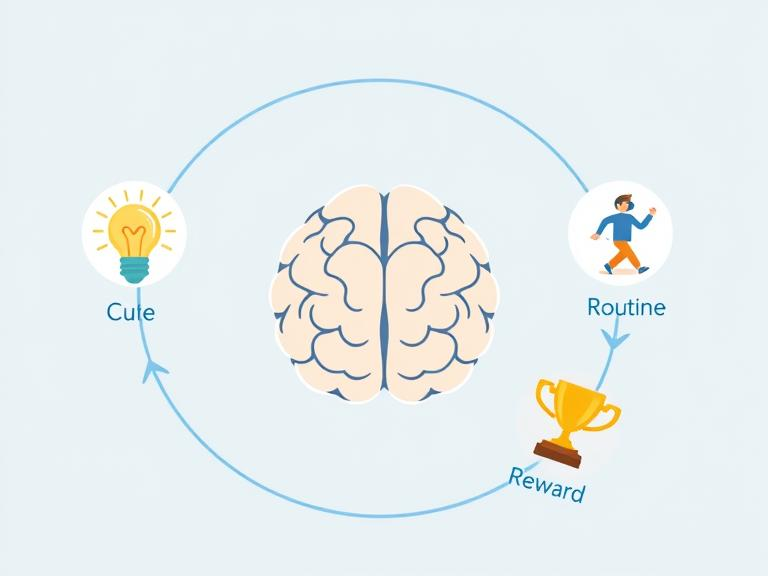
So, what’s the secret behind these effective habits? Charles Duhigg Habit Loop, a concept developed in The Power of Habit by Charles Duhigg, explaining the science of habit development in three stages:
1. Cue (Trigger)
Think of the cue as the “green light,” the routine as the “action,” and the reward as the “prize” that keeps you coming back.
The cue is the starting point, a trigger that signals your brain to activate a habit. It could be an emotional state, a specific time of day, a certain environment, or even people around you.
Examples of Cues:
- Feeling stressed (emotional cue).
- Hearing your phone’s notification sound (sound cue).
- Seeing a coffee machine in the morning (visual cue).
2. Routine (Behavior)
The routine is the action itself, what you do in response to the cue. This can be a helpful or harmful behavior.
Examples of Routines:
- Stress (cue): Smoking a cigarette (routine).
- Phone notification (cue): Instantly checking social media (routine).
- Coffee machine sight (cue): Making a cup of coffee (routine).
3. Reward (Result)
The reward reinforces the habit by providing a sense of satisfaction or relief. It triggers dopamine release, strengthening the connection between the cue and routine.
Examples of Rewards:
- Smoking a cigarette gives you calmness.
- Social media scrolling makes you feel entertained or distracted.
- Morning coffee gives you alertness.
Breaking Bad Habits: Why Changing the Routine is the Secret Weapon

Kicking a bad habit isn’t simply hard, it’s irritating. But the answer isn’t to abolish the entire habit; it’s to hack the loop by modifying the pattern.
The reason bad habits feel impossible to break is that your brain loves shortcuts. Once your brain identifies a cue and reward, it latches on, forming a mental pathway that’s hard to erase. The cue and reward are deeply wired into your brain’s memory system. Trying to remove them entirely is like deleting a file without emptying the recycle bin, it’s still there, quietly waiting to pop back up.
Instead, by swapping the routine, you satisfy your brain’s craving without feeding the bad behavior.
- Identify the Cue: Ask yourself, what triggers this behavior? Common cues include emotions (stress, boredom), time of day, or social settings.
- Pinpoint the Reward: Ask yourself, what am I really getting from this habit? It might be comfort, distraction, excitement, or relaxation.
- Swap the Routine: Replace the old habit with a new, healthier behavior that gives you a similar reward.
Example: Social Media Overload
- Cue: Feeling bored or overwhelmed.
- Old Routine: Scroll Instagram mindlessly.
- New Routine: Read a short article or text a friend.
- Reward: Mental distraction and social connection.
Write down your triggers in a journal for 7 days. Picture your brain rewiring itself each time you resist the old habit.
The key is that your brain doesn’t care how the reward happens, only that it does. According to the science of habit formation, the secret lies in swapping the routine while keeping the same reward. By successfully changing the routine, the habit loop can shift naturally, without feeling like a constant battle.
Repeat the New Behavior
Habits are built through repetition. Swapping the routine just once won’t cut it. You’ll need to repeat the new behavior until it becomes automatic. This is how your brain rewires itself.
Research shows it takes 18 to 254 days to form a new habit, with 66 days being the average. So don’t be discouraged if it takes time, consistency is key.

By understanding the psychology of habits and replacing harmful routines with positive ones, you can finally break free from those stubborn bad habits.
Why Some Habits Stick Like Super Glue

It’s all about the emotional punch. Strong emotions make habits more powerful. That’s why you never forget the exact smell of grandma’s cookies or why heartbreak makes ice cream taste ten times better.
Ever hear an old song and suddenly remember your awkward middle school dance moves? Emotions burn memories into your brain, for better or worse.
Emotions supercharge the Charles Duhigg Habit Loop. Marketers know this too, which is why tear-jerking ads get you opening your wallet faster than a magician at a kid’s party.
The Silent Hero: Your Environment

Your surroundings shape your habits more than you think. If your phone’s by your bed, guess what? Scrolling will become part of your bedtime routine. Move it to the other side of the room, and boom, better sleep habits begin.
Try this:
- Want to read more? Place a book on your pillow.
- Want to drink more water? Keep a bottle on your desk.
Tiny tweaks create powerful results. Start small, and your environment will guide your habits effortlessly, a proven strategy rooted in the science of habit formation.
Final Thoughts
The Charles Duhigg Habit Loop demonstrates how the psychology of habits impacts our daily activities. By understanding the science of habit formation, you can discover your triggers, change harmful routines, and reinforce healthy habits. Remember, habits aren’t broken overnight, but tiny, regular improvements bring lasting effects. Whether you’re seeking to raise productivity, improve health, or break bad behaviors, understanding this loop is your hidden weapon. Don’t underestimate the impact of little modifications, they may revolutionize your life. Start now by choosing one habit to alter, and unlock your full potential with smarter, purposeful decisions.





